What is Consumer Electronic PCB?
What is Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics have become an indispensable part of our daily lives, encompassing electronic devices designed for personal use, entertainment, and communication. These devices include smartphones, tablets, laptops, televisions, game consoles, digital cameras, smartwatches, and other gadgets that are ubiquitous in modern life.
Consumer electronics are usually mass-produced with an emphasis on affordability, ease of use, and aesthetics. The industry is constantly evolving and releasing new products and technologies to meet the changing needs and preferences of consumers. These devices, such as smartphones, laptops, game consoles, and smartwatches, make our lives more convenient and connected, providing us with access to information, entertainment, and communication anytime and anywhere.
What is a PCB
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is typically a flat plate made of non-conductive materials, such as fiberglass or plastic resin, with copper tracks etched on its surface. These copper tracks act as conductive pathways, connecting electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (ICs). PCBs can be either single-layer or multilayer, depending on the complexity of the electronic circuits they support. A singlelayer PCB comprises a single layer of copper on one side of the board, while a multilayer PCB has copper traces on multiple layers of the board.
Combination of Both
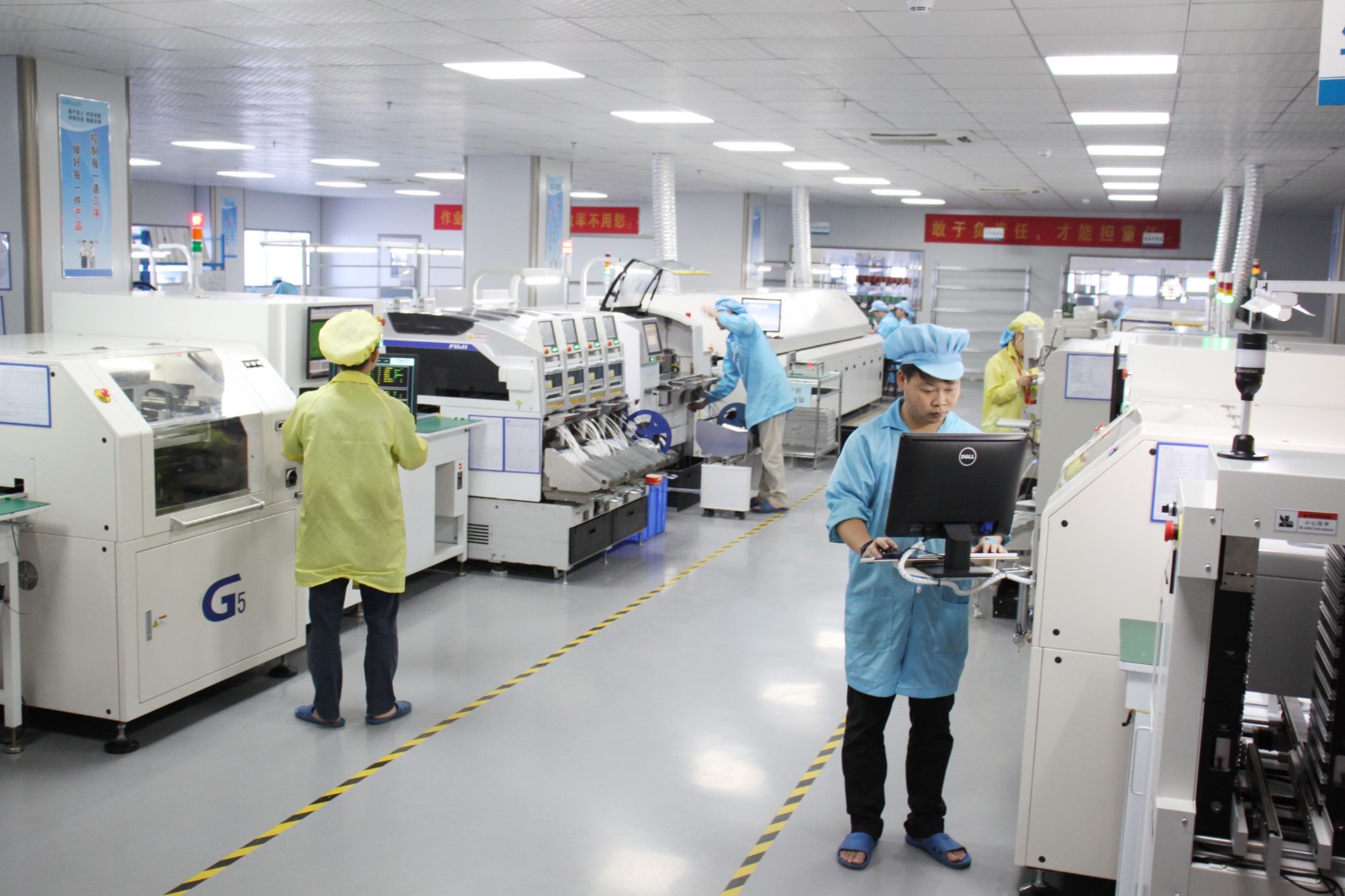
Take a moment to look around, and you will probably notice that most of the devices and items rely on electronics, and printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the foundational components for them. Think of PCBs as the heart of electronics or the bones of the human body – while PCBs themselves may not be visible, they play a vital role in ensuring the functionality of the devices and objects we touch every day. From the smartphones we use to the appliances in our homes, PCBs are hidden within and serve as the fundamental components that make these electronic devices function as intended. Behind every electronic device is a complex network of interconnected components that work together to perform various functions. The printed circuit board (PCB) is the backbone of the network, providing the platform for these components to communicate with each other.
Consumer Electronics PCBs are designed to meet the specific needs of electronic devices used by consumers. They are smaller, more compact, and more efficient than other applications such as industrial PCB and military application PCB. They are also designed to be cost-effective and mass-producible, making them ideal for manufacturers of consumer electronics.
Consumer Electronics PCB Applications
Electronic devices, such as televisions (including LED and LCD screens), home audio systems, speakers, smartphones (both old and new), intercoms, calculators, security cameras, doorbells, electric appliances (e.g., kettles, ovens, stoves, and irons), washing machines, air conditioners, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), electronic locks, proximity sensors, wearable electronics (e.g., smartwatches and smart rings), Bluetooth hands-free sets, optical devices (such as cameras and CCTV), wireless devices (e.g., Bluetooth speakers), remote controls for monitoring water levels, IR sensor-based devices, children’s toys, and e-cigarettes, rely heavily on PCBs, which are hidden within these devices.
Most of these devices utilize rigid PCB, which come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and colors (usually green, but sometimes brown in mass-produced inexpensive electronics). They are commonly used in home automation, kitchen appliances, and other household appliances and are typically single-sided or two-sided to reduce cost and limit functionality. PCBs in less advanced devices (e.g., remote controls, toys, and electric kettles) may not be as complex as those found in more advanced devices such as LED and Smart TVs, which may require multiple layers and complex Flexible PCB, ultimately leading to more expensive products.
Here are some common applications for consumer electronics PCBs:
Smartphones and Tablets: Circuit boards are essential to these devices, providing the platform for microprocessors, memory, sensors, and other electronic components that power these devices and enable them to perform a wide range of functions.
Laptops and Desktops: We are more familiar with the PCBs used in laptops and desktops, such as the motherboard, graphics card, and other internal components that provide the frame for these devices.
Gaming Consoles: Gaming consoles heavily rely on circuit boards to provide processing power and connectivity for online gaming and multimedia applications. The game card used in the Xiaobawang game console, which was popular worldwide in the 1990s, is an example of a low-end circuit board.
Smart Home Devices: Smart home devices, such as thermostats, security cameras, and smart lighting systems, rely on high-density printed circuits to provide the electronic circuitry necessary to communicate with other devices and the internet.
Audio and Video Equipment: Circuit boards are essential to audio and video equipment such as televisions, DVD players, and audio systems, providing the necessary circuitry to process and output audio and video signals.
Automotive Industry: New energy vehicles require more electronic products than traditional fuel vehicles and rely on advanced PCBs for engine management, anti-lock braking systems, car audio, GPS systems, climate control systems, and vehicle infotainment systems, such as control and monitoring systems.
Medical Equipment: Medical equipment, such as MRI machines, heart monitors, and dialysis machines, relies on medical PCB to provide the necessary circuitry to control and monitor the operation of these systems, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data generated by the equipment.